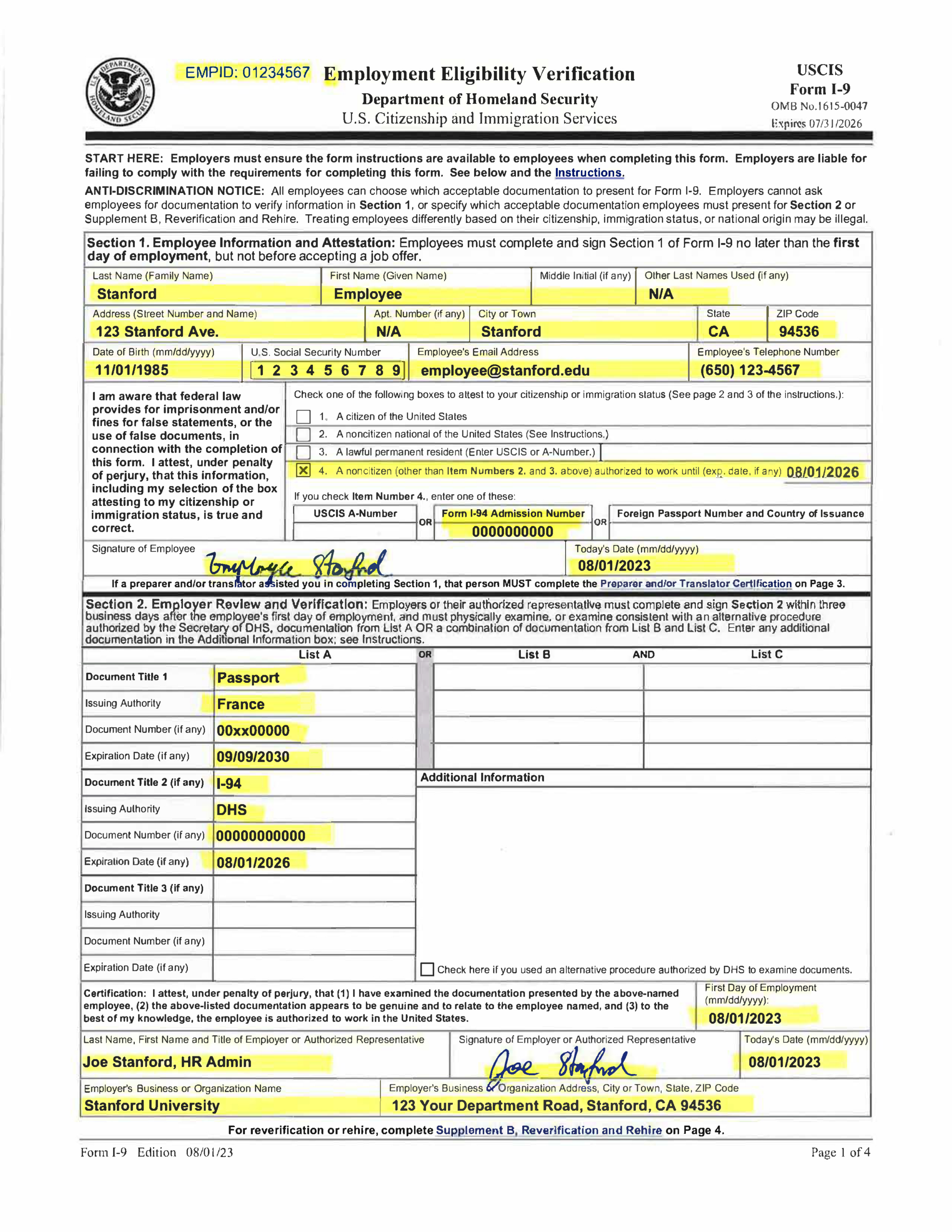
The I-9 form, officially known as the Employment Eligibility Verification form, is a crucial document required by U.S. federal law to verify the identity and legal authorization of individuals hired for employment in the United States. Here’s why it is needed:
1. Verification of Work Eligibility
The primary purpose of the I-9 form is to ensure that all employees, both U.S. citizens and non-citizens, are legally authorized to work in the United States. Employees are required to present documents to their employer as proof of their legal status and identity, which the employer must review and verify.
2. Compliance with the Immigration Reform and Control Act (IRCA)
The I-9 form was introduced as part of the IRCA in 1986, which was enacted to deter illegal immigration and unauthorized employment. This act mandates that employers must verify the employment eligibility and identity of new employees to enforce the law effectively.
3. Prevention of Discrimination
The process of completing the I-9 form is designed to prevent discrimination against employees on the basis of national origin or citizenship status. Employers are required to treat all employees equally when requesting and verifying documentation for the I-9, without prejudice or bias.
Responsibilities Involved
- Employee Responsibilities:
- Employees must accurately complete Section 1 of the I-9 form on their first day of employment (or before their first day), providing required personal details.
- They must present one or more documents from a list provided by USCIS that prove their identity and eligibility to work. The list is divided into List A (documents that prove both identity and eligibility), List B (documents that prove identity only), and List C (documents that prove eligibility to work only).
- Employer Responsibilities:
- Employers must examine the documents provided by the employee to ensure they appear genuine and relate to the employee.
- They must complete Section 2 of the form by recording the document information and verifying the employee’s eligibility within three business days of the employee’s start date.
- Employers are also responsible for retaining completed forms for a specified period (three years after the date of hire or one year after employment ends, whichever is later) and providing them for inspection if requested by authorized government officials.
Legal Implications
Failure to comply with the requirements of the I-9 form can lead to legal consequences for employers, including fines and penalties. This makes the I-9 form an integral part of the employment and hiring process, ensuring compliance with U.S. employment laws and supporting the integrity of the labor market.
Images Related to What Is A I9 Form Needed For